과제1. K-nearest Neighbor Classifier
cs231n 과제1. K-nearest Neighbor Classifier 정리
1.K-nearest Neighbor 알고리즘 설명
1.1소개
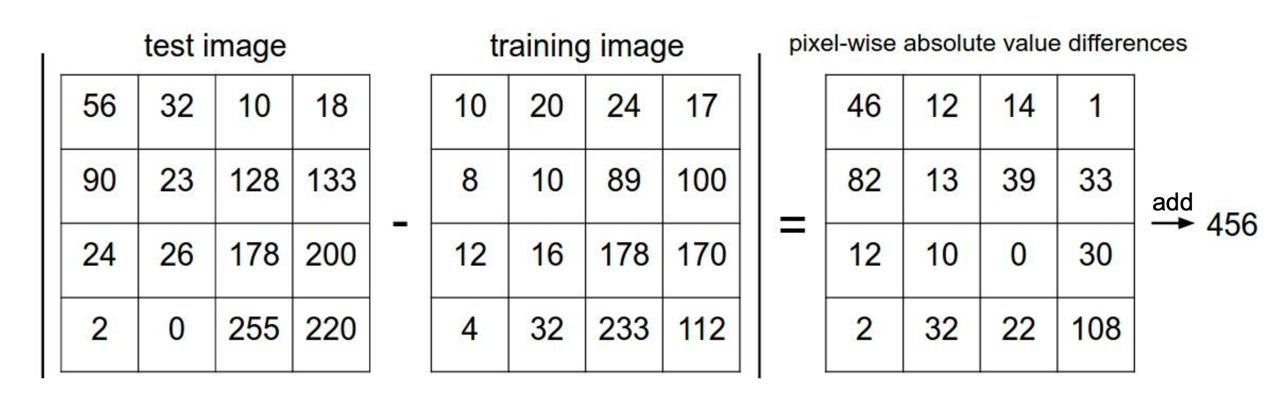 머신러닝에서 흔히 사용하는 알고리즘으로 만약 이미지 분류에서 사용하게 된다면
train 이미지, test 이미지를 빼서 두개의 이미지의 차이를 구하고, 이미지의 전체 픽셀을 더한는 구조이다.
머신러닝에서 흔히 사용하는 알고리즘으로 만약 이미지 분류에서 사용하게 된다면
train 이미지, test 이미지를 빼서 두개의 이미지의 차이를 구하고, 이미지의 전체 픽셀을 더한는 구조이다.
1.2 규제
 (cs231n )
norn 사용하는 이유는 과적합을 방지하기 위해 사용하게 합니다.
(cs231n )
norn 사용하는 이유는 과적합을 방지하기 위해 사용하게 합니다.
L1 규제는 모든 가중치 값을 절댓값을 취하고 더하게 됩니다.
L1 규제는 일부 가중치 값이 0이 되도록 유도하여 불필요한 특징을 사용하지 않도록 하여 과적합을 문제를 해결하고
L2 규제는 모든 가중치 제곱을 취하고 더하게 됩니다.
L2규제는 가중치값이 작아지도록 유도하고, 특정 feature 지나치게 않도록 유도해 과적합 문제를 해결한다.
import numpy as np
w1=np.array([0.25, 0.25,0.25,0.25])
w2 = np.array([1, 0, 0, 0])
print(f"w1 L2 규제 : ", np.sqrt(np.sum(w1 * w1)))
print(f"w2 L2 규제 : ", np.sqrt(np.sum(w2 * w2)))
w1 L2 규제 : 0.5
w2 L2 규제 : 1.0
2. train
KNearestNeighbor train 데이터를 모두 메모리 안에 저장하고 있어야한다.
self.X_train = X
self.y_train = y
print(classifier.X_train.shape)
(5000, 3072)
2.1 compute_distances_two_loops
for i in range(num_test):
for j in range(num_train):
#####################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and the jth #
# training point, and store the result in dists[i, j]. You should #
# not use a loop over dimension, nor use np.linalg.norm(). #
#####################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
distinct = X[i] - self.X_train[j]
distinct = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.power(distinct, 2)))
dists[i][j] = distinct
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return dists
모든 훈련데이터와 테스트 데이터들의 값들을 비교해서 dicts 안에 저장하고 반환한다.

2.1.1 퀴즈

- 일부 행이나 열이 눈에 띄게 더 밝아지는 거리 행렬의 구조화된 패턴에 주목하십시오. (기본 색 구성표에서 검은색은 낮은 거리를 나타내고 흰색은 높은 거리를 나타냅니다.)
- 데이터에서 뚜렷하게 밝은 행의 원인은 무엇입니까?
- 행은 test 데이터들의 집합으로 train 데이터와 차이를 계산했을때 차이(노이즈)가 클수록 밝을 수 있다.
- 열의 원인은 무엇입니까?
- 열은 train 데이터들의 집합
3. predict
label = np.argsort(dists[i])
closest_y = self.y_train[label[:k]]
y_pred[i] = np.bincount(closest_y).argmax()
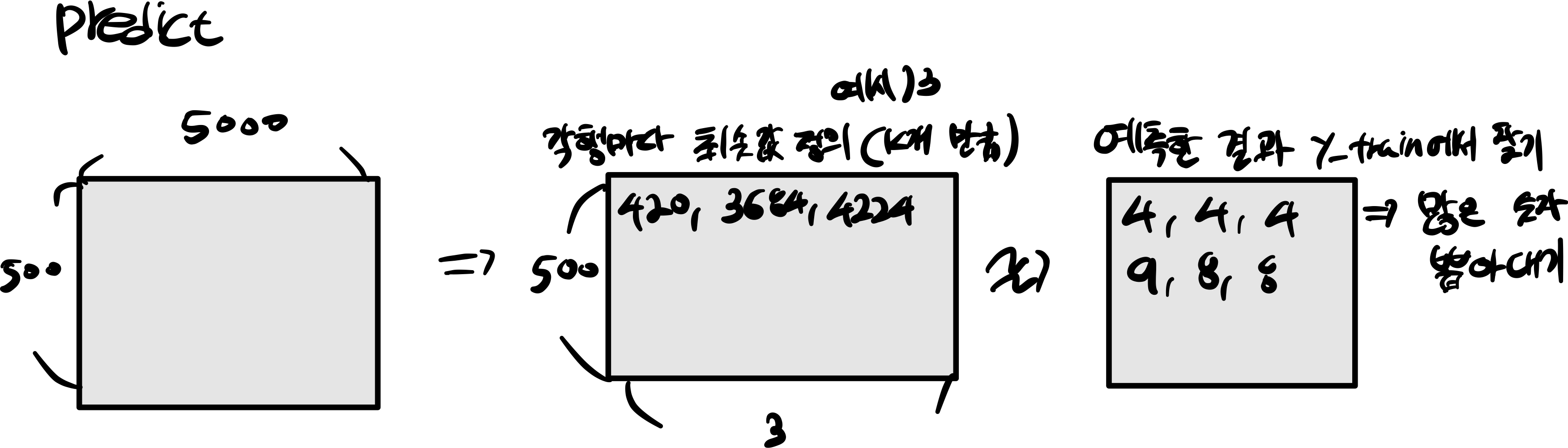 K개 만큼 최솟값 정의 하고 각각 가장 많이 예측한 값을 뽑아낸다.
K개 만큼 최솟값 정의 하고 각각 가장 많이 예측한 값을 뽑아낸다.
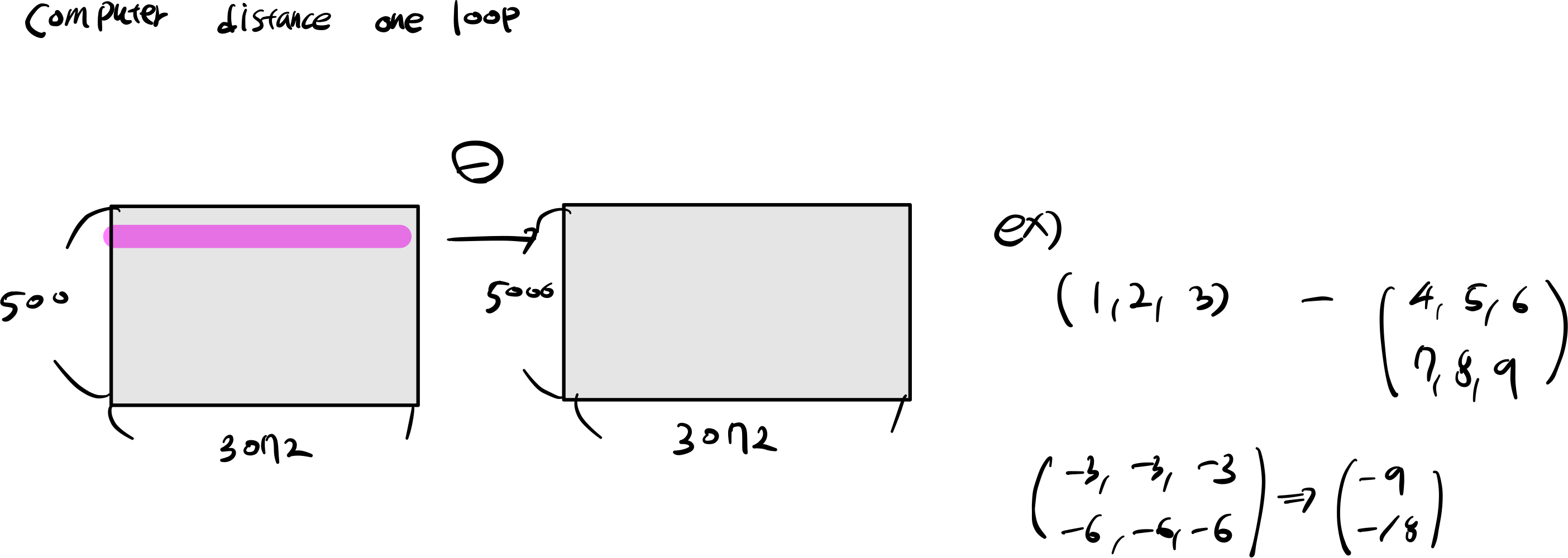
4. compute distances oneloop
for i in range(num_test):
#######################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and all training #
# points, and store the result in dists[i, :]. #
# Do not use np.linalg.norm(). #
#######################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
data = np.power(X[i] - self.X_train, 2).sum(axis=1)
dists[i, :] = np.sqrt(data)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return dists
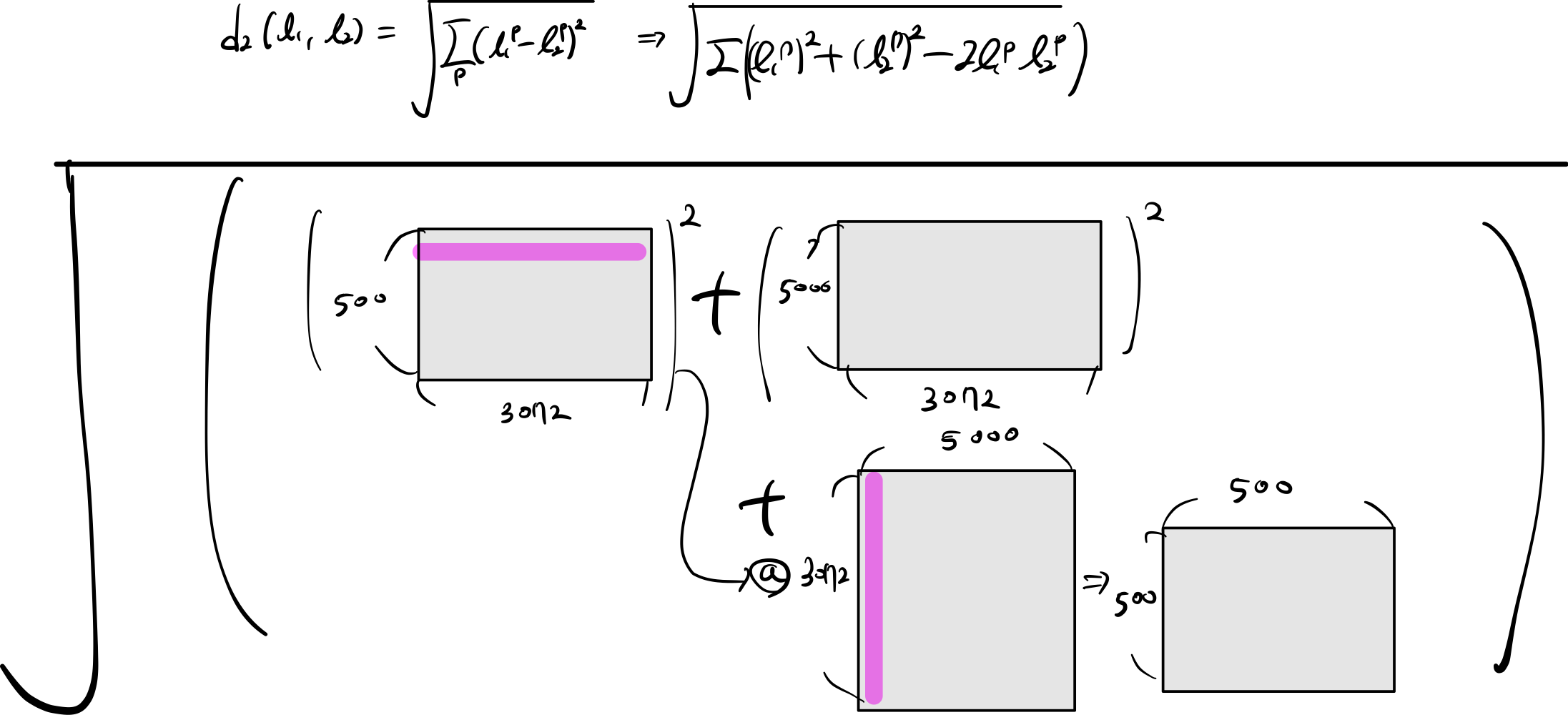
5. compute distances no loops
test_sum = np.sum(np.power(X, 2), axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
train_sum = np.sum(np.power(self.X_train, 2), axis=1)
testTrain = -2 * (np.dot(X, self.X_train.T))
dists = np.sqrt(test_sum + train_sum + testTrain)
참조
- https://cs231n.github.io/