과제2. Convolutional Neural Networks
Convolutional Neural Networks 코드 작성
1. Introduce
또한, FC 계층을 사용하여 이미지를 하나씩 처리하면 데이터에 대한 모델의 일반화 능력이 제한될 수 있습니다. 이는 모델이 이미지의 지역적 패턴이나 구조를 학습하지 못하고 각 픽셀을 독립적으로 처리하는 경향이 있습니다.
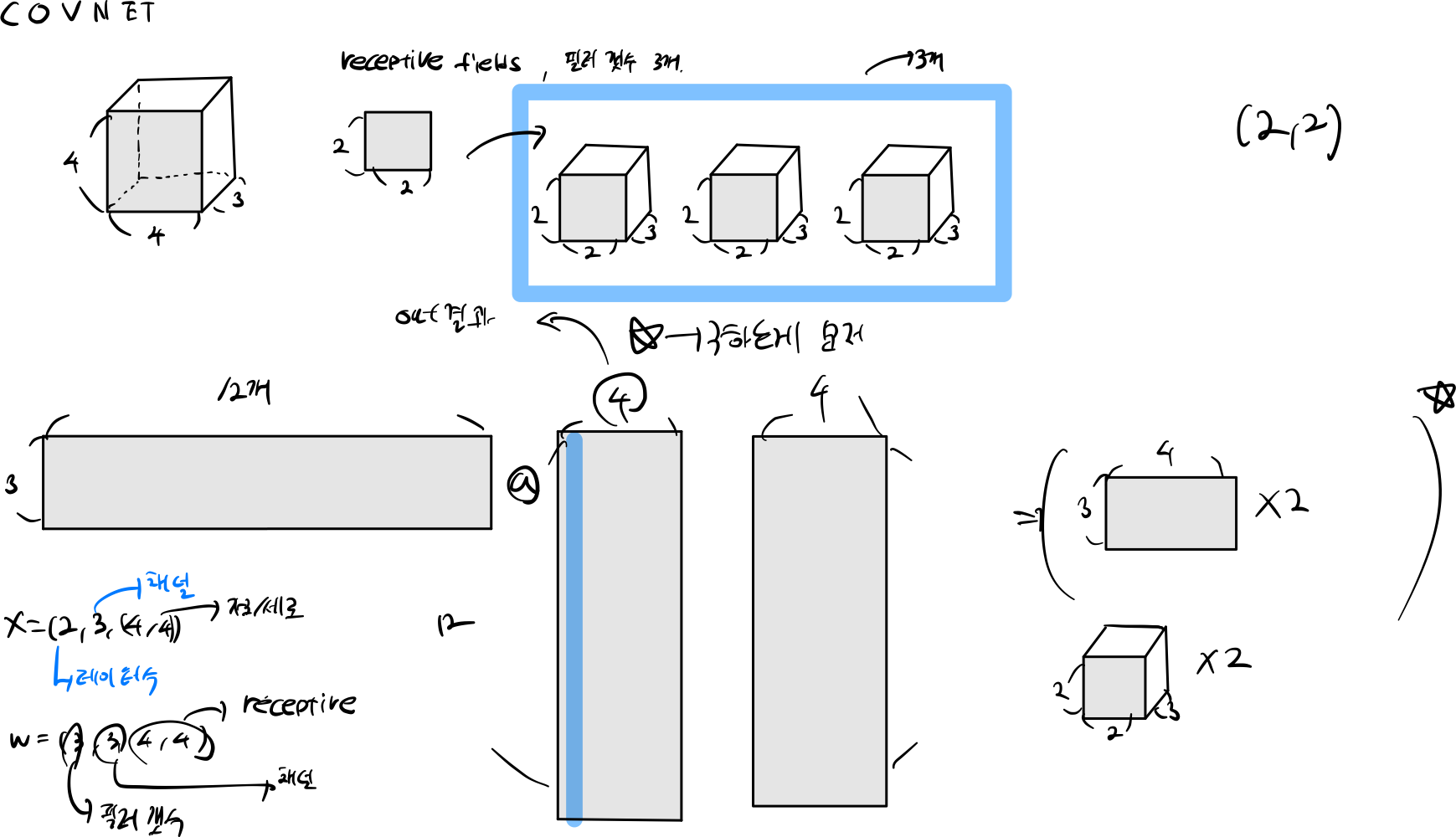
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해 개발된 것이 Convolutional Neural Network(ConvNet)입니다. ConvNet은 이미지 처리에 특화된 구조로, 합성곱 계층을 사용하여 지역적 정보를 보존하면서 파라미터 수를 효율적으로 관리합니다. 또한, 풀링 계층을 통해 공간 차원을 축소하고, 여러 개의 계층을 쌓아서 이미지의 다양한 특징을 추출할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 이미지 처리 작업에서 더 효과적인 학습과 일반화를 달성할 수 있습니다.
2. forward
def get_stride_input_data(train, N, data, stride, C, WW, HH, receptive_field):
for i in range(N):
input_data = np.lib.stride_tricks.sliding_window_view(data[i], (C, WW, HH))[:,::stride, ::stride].reshape(-1, receptive_field * C).T
train[i] = input_data
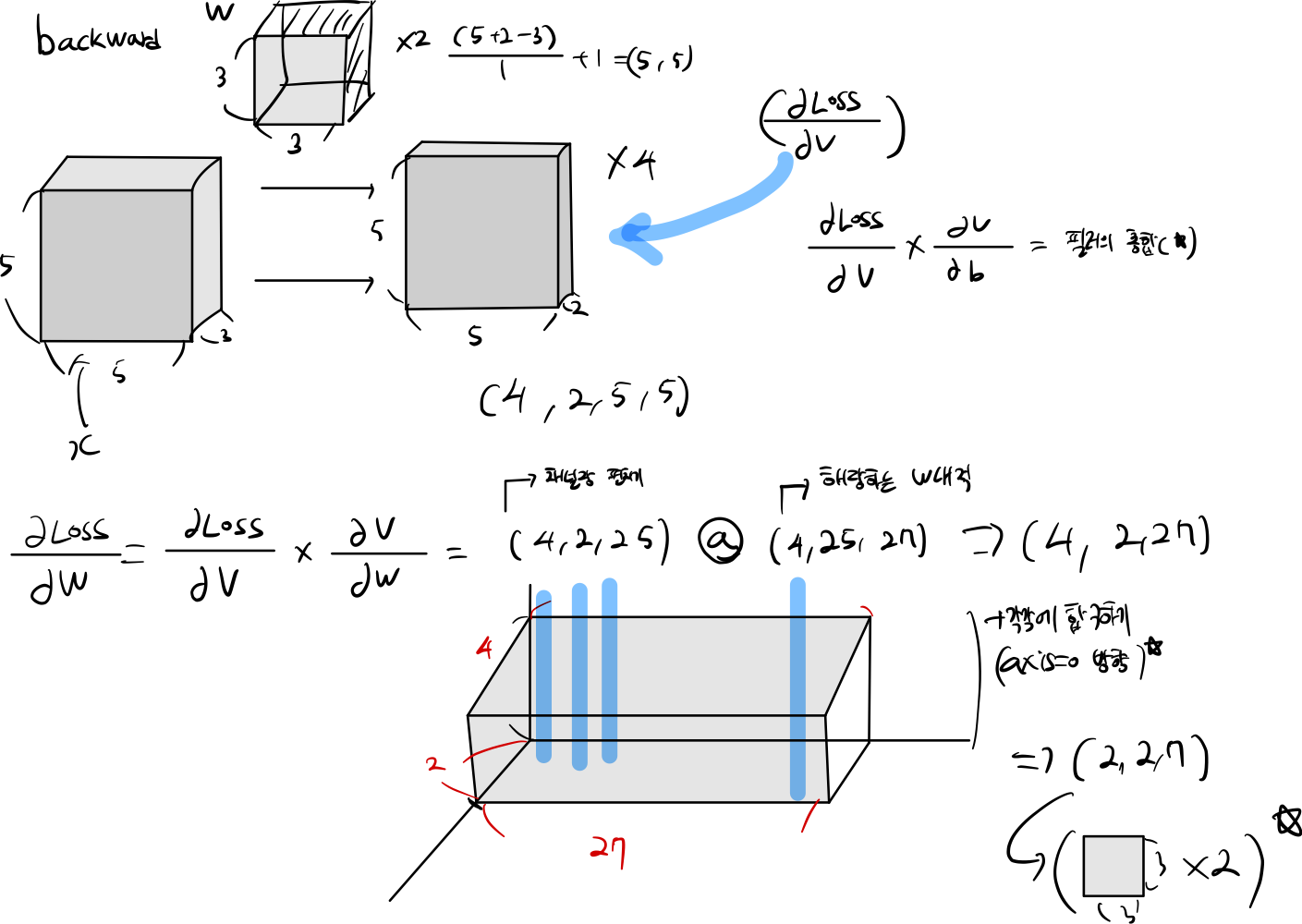
def conv_forward_naive(x, w, b, conv_param):
out = None
N, C, H, W = x.shape
F, _, HH, WW = w.shape
padding, stride = conv_param.get('pad', 0), conv_param.get('stride', 1)
width_out, height_out = int((H + 2*padding - HH) / stride + 1) ,int((W + 2*padding - WW) / stride + 1)
receptive_field = int(HH * WW)
w_out = w.reshape(int(F), int(C) * receptive_field)
x_pad = np.pad(x, ((0,), (0,), (padding,), (padding,)), mode='constant', constant_values=0)
train = np.zeros((N, receptive_field * C, width_out * height_out))
get_stride_input_data(train, N, x_pad, stride, C, WW, HH, receptive_field)
out = (w_out @ train).reshape(N, F, width_out, height_out)
b = np.expand_dims(b, axis=(2, 1))
x = train
w = w_out
out = out + b
conv_param['filter'] = (HH, WW)
conv_param['IC'] = C
conv_param['data_pad'] = x_pad.shape
cache = (x, w, b, conv_param)
return out, cache
- 입력 데이터를 4차원 이미지를 받는다. (N : 이미지 갯수, C : 채널 , H : 높이, W : 넓이)
- padding, stride 값들을 찾는다.
- output_shape 찾아낸다.
- 입력 데이터에서 receptive_field 만큼 추출한다음에 평탄화를 해야한다.
- W 가중치와 내적하거, Bais 더하게 된다.
3. backward
def get_stride_new_data(train,dx, stide, IC, FW, FH, RW, RH):
train = np.zeros(shape=train)
SH, SW = train.shape[2], train.shape[3]
index = 0
for datas in dx:
row = 0
col = 0
for j in datas.T:
new_data = j.reshape(IC, FH, FW)
if (row + FW) > SW:
col += stide
row = 0
if row > SW and col > SH:
break
train[index, :, col: col + FH, row:row + FW] += new_data
row += stide
index += 1
return train
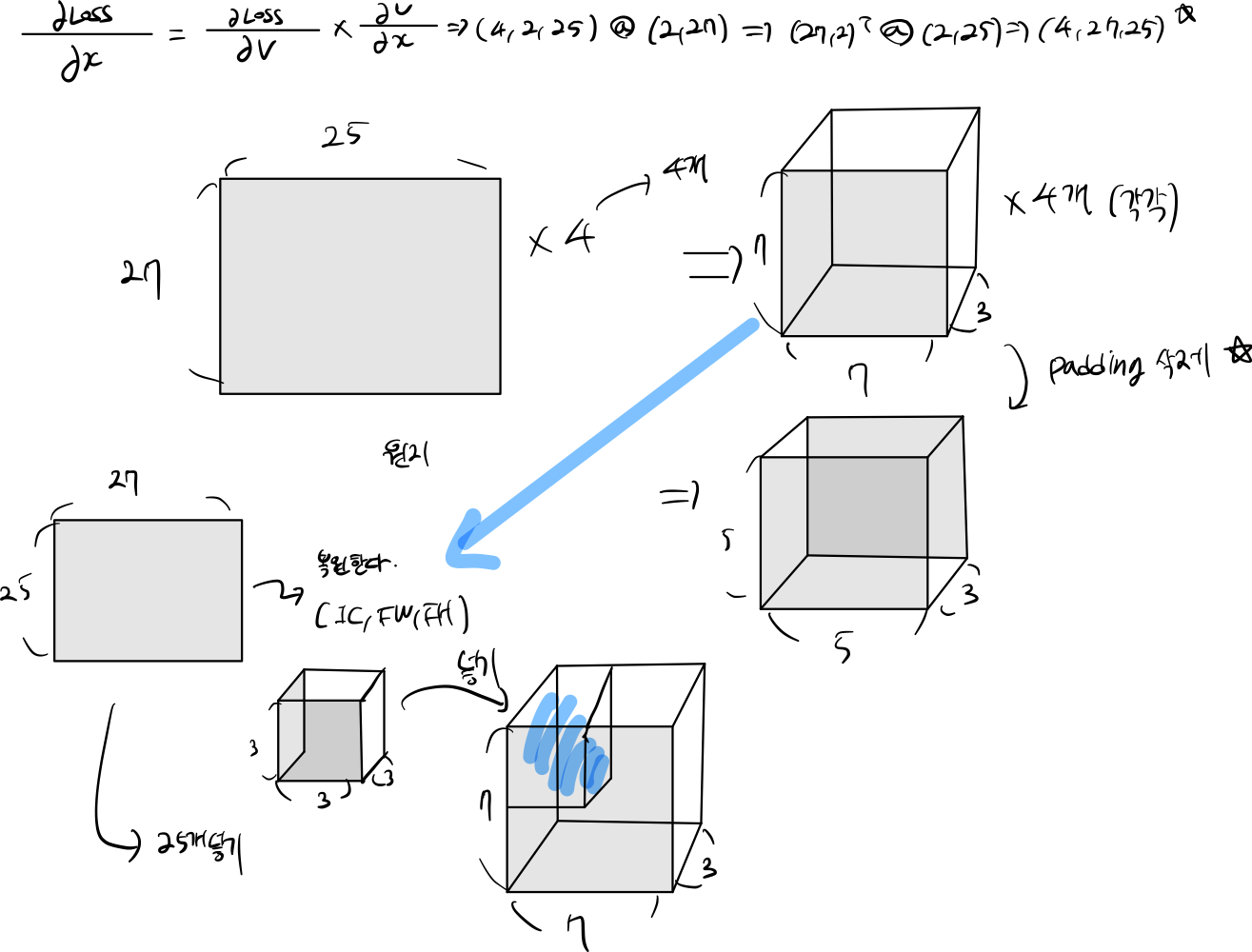
def conv_backward_naive(dout, cache):
dx, dw, db = None, None, None
###########################################################################
# TODO: Implement the convolutional backward pass. #
###########################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
x, w, b , conv_param = cache
padding, stride, receptive_field, IC, data_pad = conv_param.get('pad', 0), conv_param.get('stride', 1), conv_param.get('filter', (1,1)), conv_param.get('IC', 1), conv_param.get('data_pad', 0)
# print(IC)
RN, RC, RH, RW = dout.shape
dloss = dout.reshape(RN, RC, -1)
x_trans = np.transpose(x, (0, 2, 1))
dw = (dloss @ x_trans).sum(0)
dw = dw.reshape(RC, IC, receptive_field[0],receptive_field[1])
db = dout.sum(axis=(0, 2,3))
dx = (w.T @ dloss)
x_pad = get_stride_new_data(data_pad, dx, stride, IC, receptive_field[0], receptive_field[1], RW, RH)
train = x_pad
dx = train[:, :, padding:-padding ,padding:-padding]
return dx, dw, db